Technology Trends in Diabetes Management: Artificial Pancreas, Smart Insulin Pens, etc.

Technology Trends in Diabetes Management: Artificial Pancreas, Smart Insulin Pens, etc.
1. Introduction to Technology in Diabetes Management
Technology is rapidly transforming the landscape of diabetes management, offering innovative solutions to help individuals better monitor and control their condition. From the development of artificial pancreas systems to the advent of smart insulin pens, continuous glucose monitoring devices, and telemedicine platforms, the integration of technology has the potential to revolutionize diabetes care. This article explores the latest trends in technology-driven diabetes management, highlighting the benefits, challenges, and ethical considerations associated with these advancements. Additionally, we will delve into the future outlook and emerging technologies that hold promise for enhancing the lives of individuals living with diabetes.
Managing diabetes can be a challenging task that requires constant monitoring and careful control of blood sugar levels. Fortunately, advancements in technology have provided new tools and devices to make this process easier and more efficient. From artificial pancreas systems to smart insulin pens and continuous glucose monitoring, these technological innovations are revolutionizing diabetes management.
2. The Promise of the Artificial Pancreas
How Does an Artificial Pancreas Work?
Benefits and Challenges of Artificial Pancreas Technology
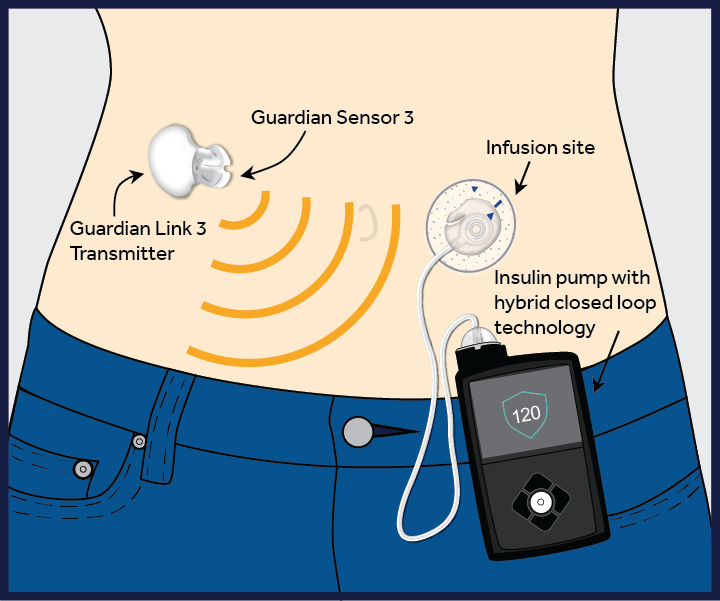
Imagine a device that can mimic the functions of a healthy pancreas, constantly monitoring blood sugar levels and automatically delivering the right amount of insulin when needed. This is the promise of the artificial pancreas, also known as a closed-loop insulin delivery system. Combining a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) and an insulin pump, the artificial pancreas can continuously adjust insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings, providing better blood sugar control and reducing the risk of hypo- or hyperglycemia.
While the artificial pancreas shows great potential in improving diabetes management, there are still challenges to overcome. Issues such as the accuracy of glucose sensors and insulin infusion sets, as well as the need for regular calibration and maintenance, can impact the effectiveness of the system. However, ongoing research and development aim to address these challenges, paving the way for a more autonomous and reliable artificial pancreas technology.
3. Smart Insulin Pens: Revolutionizing Insulin Delivery
Overview of Smart Insulin Pens
Features and Benefits of Smart Insulin Pens
Integration with Mobile Apps and Data Tracking
Gone are the days of manually adjusting insulin dosages with syringes. Smart insulin pens have emerged as a game-changer in insulin delivery, offering more accurate and convenient administration. These pens come equipped with electronic features, such as memory and dose tracking, that allow users to monitor their insulin intake more effectively. Some models even offer reminders and alerts to ensure timely insulin administration.
The benefits of smart insulin pens go beyond improved accuracy and ease of use. They provide valuable data on insulin dosage patterns, which can help healthcare professionals and individuals better understand their diabetes management. By integrating with mobile apps and other digital platforms, smart insulin pens enable seamless data sharing and monitoring, facilitating more informed decisions and personalized care.
4. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Advancements in Sugar Tracking
Introduction to Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
Types of CGM Systems Available
Advantages and Limitations of CGM Technology
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems have revolutionized the way people with diabetes track their blood sugar levels. Unlike traditional fingerstick testing, CGM provides real-time glucose readings, allowing individuals to monitor their blood sugar throughout the day. These systems consist of a tiny sensor inserted under the skin, which measures interstitial glucose levels, and a transmitter that sends the data to a receiver or smartphone.
There are different types of CGM systems available, ranging from standalone devices to integrated systems that work alongside insulin pumps. Each system has its unique features and characteristics, offering users options that suit their individual needs and preferences.
The advantages of CGM technology include improved glucose control, reduced hypoglycemia risk, and the ability to detect trends and patterns in blood sugar levels. However, CGM systems also have limitations, such as occasional calibration errors and the need for regular sensor replacement. Despite these limitations, CGM technology has significantly enhanced diabetes management and played a crucial role in improving the quality of life for people with diabetes.5. Telemedicine and Mobile Applications: Enhancing Diabetes Care
Telemedicine: Bridging the Gap in Healthcare Access
In the age of smartphones and high-speed internet, visiting the doctor’s office may soon become a thing of the past. Telemedicine is revolutionizing healthcare by allowing patients to consult with healthcare professionals remotely. For individuals with diabetes, this means easier access to medical advice, medication management, and continuous support. No more sitting in waiting rooms or struggling to find transportation to the clinic; with telemedicine, healthcare is just a phone call (or video chat) away.
Mobile Applications for Diabetes Management
Gone are the days of carrying bulky logbooks to track blood sugar levels and meal plans. Mobile applications specifically designed for diabetes management are making life easier for those with the condition. These apps allow users to monitor blood glucose levels, track food intake, record exercise, and even set reminders for medication. With a few taps on their smartphones, individuals with diabetes can have a comprehensive overview of their health in the palm of their hands.
Benefits and Considerations of Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring is another game-changer in diabetes management. With the help of wearable devices and connected technology, individuals can continuously monitor their blood sugar levels, heart rate, and other vital signs. This real-time data can be shared with healthcare providers, enabling them to make informed decisions about treatment plans. While remote monitoring offers convenience and personalized care, it is important to consider the accuracy and reliability of the devices used, as well as the privacy and security of the data collected.
6. Data Integration and Analytics: Harnessing Technology for Improved Management
The Importance of Data Integration in Diabetes Management
In the era of big data, collecting and analyzing information plays a vital role in managing diabetes effectively. Data integration involves consolidating information from various sources, such as glucose meters, wearable devices, and electronic health records, into a single platform. This holistic view of a patient’s health allows healthcare professionals to identify patterns and trends, optimize treatment plans, and make evidence-based decisions.
Utilizing Data Analytics for Personalized Treatment Plans
Data analytics takes data integration to the next level by utilizing advanced algorithms to analyze vast amounts of information. By identifying correlations and patterns, data analytics can help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to each individual’s unique needs. This personalized approach improves patient outcomes and enhances the efficiency of diabetes management.
Privacy and Security Concerns in Data Management
While data integration and analytics offer significant benefits, it is crucial to address privacy and security concerns. With sensitive health information being stored and transmitted electronically, safeguarding patient data is of utmost importance. Robust security measures, encrypted communication channels, and strict adherence to privacy regulations are essential to maintain the trust of patients and protect their sensitive information.
7. Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Technology-driven Diabetes Management
Ensuring Accessibility and Affordability of Technological Solutions
As technology continues to advance, it is essential to ensure that everyone, regardless of socioeconomic status, has access to the latest diabetes management solutions. Promoting affordability and accessibility can help bridge the digital divide and empower individuals from all backgrounds to take control of their health.
Ethical Considerations in Data Collection and Usage
With the abundance of health data being collected, ethical considerations come to the forefront. It is essential to prioritize patient privacy, obtain informed consent, and use data responsibly. Striking a balance between data collection and patient autonomy is crucial for maintaining trust and ethical standards in technology-driven diabetes management.
8. Future Outlook: Emerging Technologies in Diabetes Care
Promising Technologies on the Horizon
The future of diabetes care is looking bright, with several exciting technologies on the horizon. From smart contact lenses that monitor blood sugar levels to implantable devices that deliver insulin automatically, researchers and innovators are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. These emerging technologies hold the promise of making diabetes management even more seamless and effective.
Exploring Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Diabetes Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize diabetes management. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make real-time predictions, empowering healthcare providers to deliver personalized treatment plans. By harnessing AI and ML, the future of diabetes management may involve smart algorithms that continuously learn and adapt to each individual’s changing needs, leading to improved outcomes and quality of life. In conclusion, the advancements in technology have opened up new possibilities in diabetes management, offering individuals with diabetes improved control, convenience, and quality of life. From artificial pancreas systems to smart insulin pens, continuous glucose monitoring devices, and telemedicine platforms, these technological innovations have transformed the way diabetes is monitored and treated. However, as we embrace these advancements, it is essential to address challenges such as accessibility, affordability, and ethical considerations surrounding data privacy. Looking ahead, the future of diabetes care holds even more promise with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. With continued research and innovation, technology will continue to play a vital role in improving the lives of individuals living with diabetes.
FAQ
1. How do smart insulin pens work?
Smart insulin pens are designed to simplify insulin delivery for individuals with diabetes. These pens are equipped with features such as dose memory, Bluetooth connectivity, and integration with mobile apps. Users can track their insulin doses, set reminders, and monitor their injection history. Some smart pens even provide real-time feedback and guidance on injection techniques, helping individuals maintain proper insulin administration.
2. Are continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices accurate?
CGM devices have significantly improved the accuracy of blood sugar monitoring compared to traditional fingerstick methods. These devices use tiny sensors placed under the skin to measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid. While CGM technology has advanced in terms of accuracy, occasional discrepancies may still occur when compared to blood glucose meter readings. It is essential to calibrate CGM devices regularly and cross-reference results with fingerstick tests for optimal accuracy.
3. What are some key ethical considerations in technology-driven diabetes management?
Privacy and data security are crucial ethical concerns in technology-driven diabetes management. As personal health information is collected and transmitted, it is essential to ensure that data is protected from breaches and misuse. Additionally, accessibility and affordability of technological solutions must be addressed to ensure that individuals from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds can benefit from these advancements in diabetes care.
4. Will emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play a role in diabetes management?
Yes, AI and ML hold great potential in transforming diabetes management. These technologies can analyze large amounts of data, identify patterns, and make personalized treatment recommendations. AI and ML algorithms can assist healthcare providers in predicting hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic events, optimizing insulin dosing, and generating insights into an individual’s unique response to diabetes treatments. However, further research and development are necessary to fully harness the power of AI and ML in diabetes care.
