Exploring the Connection Between Diabetes and Peripheral Neuropathy
1. Introduction to Diabetes and Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetes and peripheral neuropathy are closely intertwined conditions affecting millions worldwide. Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, can lead to nerve damage known as peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy refers to the dysfunction or damage of the peripheral nerves, resulting in various symptoms such as tingling, numbness, pain, and muscle weakness. This article explores the complex connection between diabetes and peripheral neuropathy, delving into the underlying mechanisms, common symptoms, diagnostic methods, management strategies, and potential preventive measures. By gaining a deeper understanding of this relationship, individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals can effectively navigate the challenges posed by peripheral neuropathy and improve overall quality of life.
1. Introduction to Diabetes and Peripheral Neuropathy
1.1 What is Diabetes?
Living with diabetes can feel like having an unwelcome roommate who refuses to leave. It’s a long-term condition that disrupts your blood sugar levels, forcing you to constantly work to keep them in check. Diabetes occurs when your body doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively.
1.2 Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
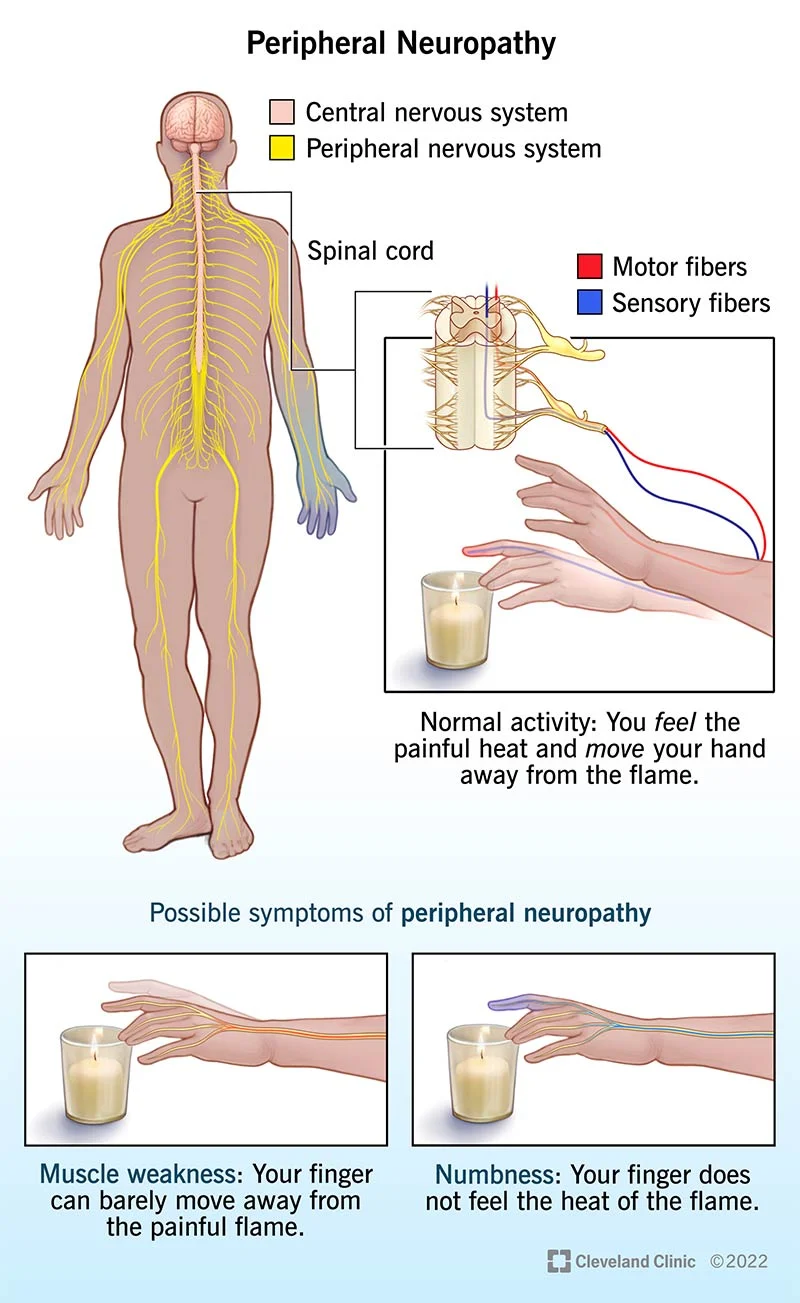
Imagine walking on a sandy beach, feeling the gentle tickle of sand between your toes. Now, replace the beach with a bed of pins and needles. This is what peripheral neuropathy feels like, a condition in which the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord are damaged.
2. Understanding the Pathophysiology of Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes
2.1 The Role of Hyperglycemia in Nerve Damage
Hyperglycemia, the arch-nemesis of diabetes management. When your blood sugar levels go sky-high, it’s like a tidal wave crashing into your nerves. The excess sugar wreaks havoc, damaging the blood vessels that supply those precious nerves with much-needed nourishment.
2.2 Neurovascular Factors and Nerve Degeneration
The blood vessels we talked about earlier are very important for maintaining the health of your nerves. When these vessels are impaired, it’s like having a blocked pipeline, which leads to inflammation, starvation, and eventually death of the nerves.
3. Common Symptoms and Complications of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
3.1 Sensory Symptoms: Tingling, Numbness, and Pain
Ever had that feeling when your foot falls asleep and you experience that delightful tingling sensation? Well, with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, it’s like your foot took a permanent nap. You might also experience numbness and pain that feels like a not-so-friendly game of tag between hot coals and ice cubes.
3.2 Motor Symptoms: Muscle Weakness and Loss of Coordination
Coordinating a dance routine? Forget it. With peripheral neuropathy, your muscles might decide to play their own tune. You’ll be left with weakness, difficulty moving those limbs, and maybe even tripping over your own two feet.
3.3 Autonomic Symptoms: Digestive and Cardiovascular Issues
Imagine your body’s autonomic nervous system as a control freak, making sure everything runs smoothly without you having to think about it. But with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, it’s like your control freak went on a vacation. Digestive issues, like constipation or diarrhea, and heart problems can become your unwelcome travel companions.
4. Diagnosis and Screening Methods for Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetic Patients
4.1 Clinical Evaluation and Medical History
Now, before you panic and think you’re on an episode of House, diagnosis starts with a good ol’ conversation with your doctor. They’ll ask about your symptoms and medical history, and might even throw in some witty banter to lighten the mood. Don’t worry, you won’t need to solve any mysterious medical cases.
4.2 Sensory and Motor Function Tests
You’re about to undergo some sensory tests to determine how well you can feel different sensations such as a light touch or a pinprick. Don’t worry, it’s not a guessing game. They’ll also evaluate your motor skills to see if you can move your limbs proficiently or if you’re struggling like a toddler learning to walk.
4.3 Electrophysiological Studies and Nerve Biopsy
If the doctor wants to dig deeper (literally), they might whip out some fancy tests like nerve conduction studies or electromyography. These tests measure the electrical activity in your nerves and muscles, giving them a closer look at what’s really going on. And hey, if they’re feeling adventurous, they might even suggest a nerve biopsy, just for fun. Just kidding, it’s not really fun, but it can provide valuable information.
So there you have it, a glimpse into the mysterious connection between diabetes and peripheral neuropathy. Remember, managing your diabetes is key to preventing or slowing down the progression of this nerve-wracking condition. Stay tuned, folks, and keep those blood sugar levels in check!
5. Managing and Treating Peripheral Neuropathy in Individuals with Diabetes
Living with diabetes is tough enough, but when peripheral neuropathy enters the mix, things can get even trickier. Fortunately, there are several strategies that can help manage and treat this condition.
5.1 Glycemic Control and Sugar Management
Sorry to break it to you, but keeping your blood sugar in check is not just about avoiding those tempting donuts. Proper glycemic control is crucial for managing peripheral neuropathy. By closely monitoring your blood sugar levels and following a healthy diet, you can help prevent further nerve damage and reduce symptoms.
5.2 Medications for Symptom Relief and Nerve Repair
When the tingling, numbness, and pain in your hands and feet become unbearable, medications can come to the rescue. There are several options available that can provide relief from these symptoms and even help repair damaged nerves. Talk to Addysdiabeteshealthstore to find the right medication for you.
5.3 Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Techniques
Physical therapy may sound like torture, but trust me, it can work wonders for peripheral neuropathy. Through exercises and specialized techniques, physical therapists can help improve your balance, strength, and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and improving your overall quality of life.
6. Lifestyle Modifications and Self-care Strategies for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Living with diabetic peripheral neuropathy requires some lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies to keep those pesky symptoms at bay.
6.1 Diet and Nutrition Recommendations
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet can help manage peripheral neuropathy symptoms. You don’t have to live on a diet of kale and quinoa, but incorporating nutrient-rich foods, watching portion sizes, and avoiding excessive sugar can make a significant difference.
6.2 Foot Care and Proper Shoe Selection
Having foot problems with neuropathy is like trying to walk with banana peels on your shoes. It’s a recipe for disaster. Proper foot care and shoe selection are essential to prevent injuries, infections, and ulcers. So, put those fancy stilettos aside and opt for comfortable, supportive footwear.
6.3 Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
I know, exercise is not everyone’s cup of tea. But staying physically active can help improve blood circulation and reduce symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. Plus, you don’t have to be a gym fanatic—just find an activity you enjoy, whether it’s dancing, swimming, or even walking your dog.
7. Preventive Measures and Risk Reduction Strategies for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
By taking some simple measures, you can reduce your risk of developing diabetic peripheral neuropathy or help slow down its progression.
7.1 Early Detection and Monitoring of Diabetes
Regular check-ups, blood tests, and keeping an eye on your symptoms can help identify diabetes early on, allowing for prompt treatment and potentially preventing peripheral neuropathy.
7.2 Optimal Diabetes Control and Sugar Regulation
However, by maintaining optimal diabetes control and regulating your blood sugar levels, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing peripheral neuropathy or halt its progression.
7.3 Lifestyle Changes to Minimize Nerve Damage
By making adjustments to your lifestyle, such as quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and managing stress, you can minimize the risk of nerve damage and potential complications.
8. Emerging Research and Future Directions in Diabetes and Peripheral Neuropathy
Fortunately, research into diabetes and peripheral neuropathy is constantly evolving, bringing hope for new treatments and improved management strategies. Keep an eye on the future, my friend, and stay tuned for exciting developments in this field. Who knows what groundbreaking discoveries lie ahead?
In conclusion, understanding the connection between diabetes and peripheral neuropathy is crucial for effectively managing and addressing the associated challenges. By implementing proper glycemic control, utilizing appropriate medications, engaging in physical therapy, and adopting lifestyle modifications, individuals with diabetes can minimize the impact of peripheral neuropathy on their daily lives. Furthermore, continued research and advancements in the field hold promise for improved diagnostic methods and innovative treatment options. By prioritizing prevention, early detection, and comprehensive care, we can strive towards a future where the burden of diabetic peripheral neuropathy is significantly reduced, enabling individuals to live healthier and more fulfilling lives.
FAQ
1. Can peripheral neuropathy occur in individuals without diabetes?
Yes, peripheral neuropathy can occur in individuals without diabetes. While diabetes is one of the leading causes of peripheral neuropathy, there are other factors such as genetic predisposition, autoimmune disorders, certain medications, and vitamin deficiencies that can contribute to the development of peripheral neuropathy.
2. How is peripheral neuropathy diagnosed in individuals with diabetes?
Diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy in individuals with diabetes typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history assessment, and specialized tests. These tests may include sensory and motor function assessments, nerve conduction studies, electromyography (EMG), and occasionally nerve biopsies. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to accurately diagnose and determine the extent of peripheral neuropathy.
3. Can peripheral neuropathy be cured?
Peripheral neuropathy caused by diabetes cannot be completely cured, but effective management strategies can help alleviate symptoms, slow down the progression of nerve damage, and improve quality of life. Proper blood sugar control, medications for symptom relief, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications can all play a significant role in managing peripheral neuropathy symptoms and preventing further complications reach out to addysdiabeteshealthstore on how to solve problems like this.
4. Are there any preventive measures for diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
While it may not always be possible to prevent diabetic peripheral neuropathy entirely, there are preventive measures that individuals with diabetes can take to reduce their risk of developing or worsening neuropathy. These measures include maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and maintaining proper foot care and hygiene. Regular check-ups and early detection of diabetes can also help in minimizing the risk of peripheral neuropathy.